Reits vs physical property: real estate investment breakdown
 REITs vs. Physical Property: A Real Estate Investment Breakdown
REITs vs. Physical Property: A Real Estate Investment Breakdown
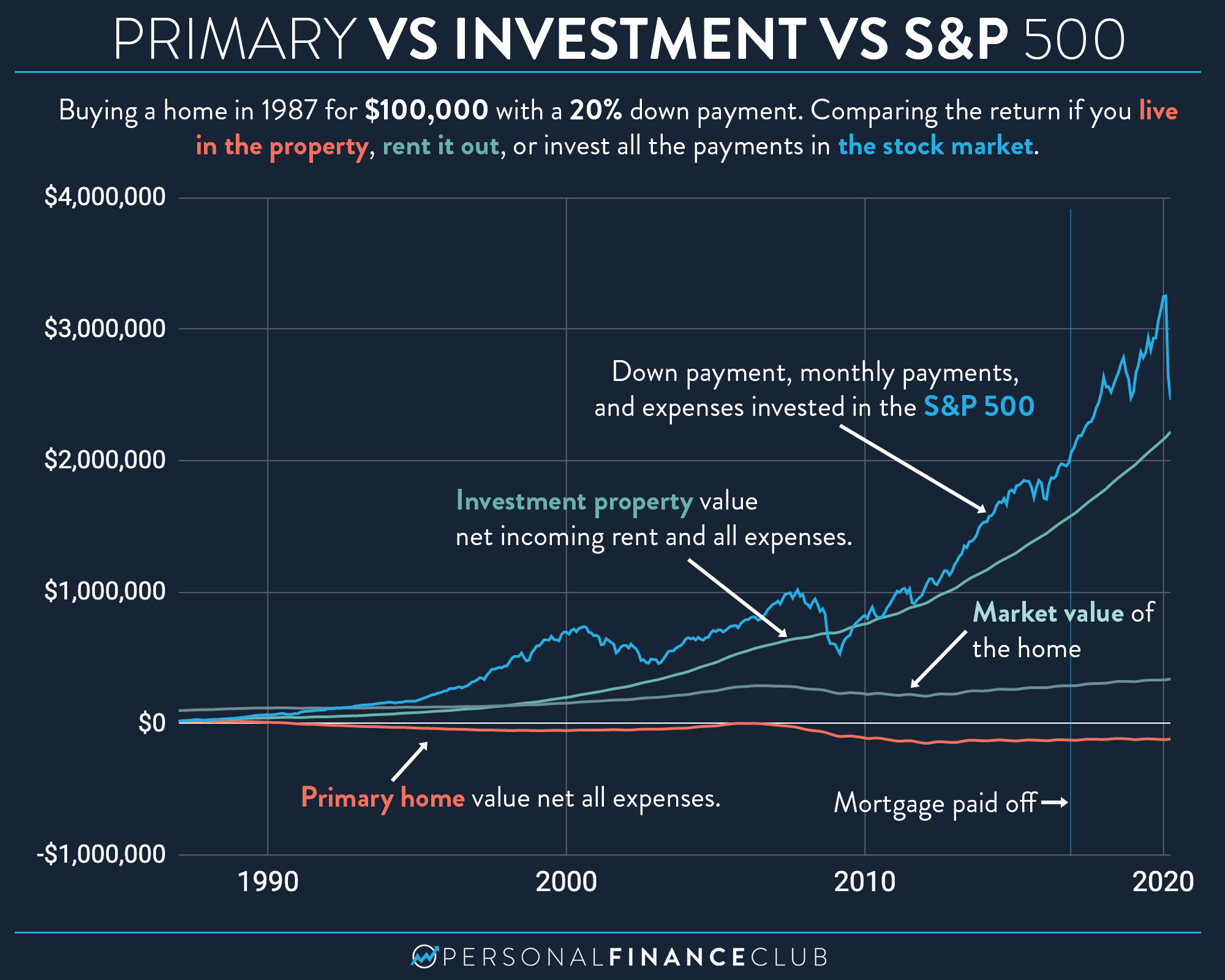
This analysis examines the contrasting approaches of investing in real estate through Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) and direct ownership of physical properties. Both offer pathways to participation in the real estate market, but their characteristics, risks, and returns differ significantly. Understanding these differences is crucial for investors seeking to optimize their portfolios and align their investments with individual financial goals and risk tolerance. The following sections will detail the key distinctions and considerations for each approach, providing a framework for informed decision-making.
Historically, direct property ownership was the primary method of real estate investment. However, the emergence of REITs, particularly in the latter half of the 20th century, provided a more liquid and accessible alternative. This diversification within the real estate investment landscape expanded opportunities for a wider range of investors. The evolution of these two investment strategies reflects broader changes in capital markets and investor preferences.
The subsequent sections will delve into the specifics of REITs versus direct property investment, exploring factors such as liquidity, management responsibilities, capital requirements, tax implications, and potential returns. A frequently asked questions section and a collection of practical tips will further enhance understanding and aid in investment planning.
FAQs about Real Estate Investment Approaches
This section addresses common questions concerning the relative merits of investing in REITs versus physical properties.
Question 1: What is the liquidity of each investment type?
REITs offer significantly higher liquidity compared to physical properties. REIT shares trade on major exchanges, allowing for relatively quick buying and selling. Conversely, selling physical property often involves a prolonged process, including marketing, negotiations, and closing procedures, potentially resulting in considerable delays and transaction costs.
Question 2: What are the management requirements?
Investing in REITs requires minimal management effort; investors simply buy and sell shares. Physical property ownership, however, demands active management, encompassing tasks such as property maintenance, tenant relations, rent collection, and property tax payments. This can be time-consuming and require specialized knowledge.
Question 3: What are the typical capital requirements?
REIT investments typically require significantly lower initial capital outlay than purchasing physical properties. Investors can access the real estate market with smaller amounts of capital through REITs. Conversely, direct property ownership demands a substantially larger initial investment, often necessitating financing through mortgages or loans.
Question 4: How are taxes handled differently?
REITs are typically structured to pass through most of their income to shareholders, avoiding double taxation. However, tax implications for physical property ownership are complex and vary considerably depending on factors like depreciation, capital gains, and property taxes. Professional tax advice is often recommended.
Question 5: What are the potential returns and risks?
Both REITs and physical properties offer potential for capital appreciation and income generation. However, the risk profiles differ. REITs are generally subject to market fluctuations, while physical properties carry risks associated with property management, vacancy rates, and market conditions in specific geographic locations. Diversification helps mitigate some of these risks.
Question 6: Which is more suitable for long-term versus short-term investment horizons?
REITs are more suited to investors with both short-term and long-term investment horizons due to their liquidity. Physical properties are generally considered more suitable for long-term investment strategies due to the time and effort required to liquidate them.
The answers highlight the need for careful consideration of individual financial goals and risk tolerance when choosing between these investment vehicles.
Tips for Navigating Real Estate Investment Strategies
These tips provide a practical guide for investors navigating the choices between REITs and direct property ownership.
Tip 1: Conduct thorough due diligence. For REITs, examine the company's financial statements, management team, and portfolio composition. For physical properties, assess location, property condition, rental market analysis and potential for future appreciation.
Tip 2: Diversify your investments. Don't put all your eggs in one basket. Consider diversifying across different REIT sectors or geographic locations for physical properties.
Tip 3: Understand your risk tolerance. REITs generally offer lower risk compared to direct property ownership but also may have lower potential returns.
Tip 4: Seek professional advice. Consult with a financial advisor to help determine the most appropriate investment strategy based on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and overall portfolio.
Tip 5: Factor in transaction costs. Remember to consider brokerage commissions, property taxes, and other fees associated with both REIT and physical property investments.
Tip 6: Monitor your investments regularly. Stay informed about market trends and the performance of your investments, making adjustments as necessary.
Tip 7: Consider long-term growth potential. Real estate, in both forms, historically demonstrates long-term growth, though short-term fluctuations are expected. This should be a key factor in the decision-making process.
Following these tips can contribute to a more successful and informed investment approach.
Conclusion on Real Estate Investment Strategies
This analysis has explored the key differences between investing in REITs and directly owning physical properties. Both offer distinct advantages and disadvantages concerning liquidity, management requirements, capital needs, tax implications, and risk profiles. The optimal choice depends on individual circumstances, financial goals, and risk tolerance.
Ultimately, a well-informed decision hinges on a thorough understanding of one's investment objectives and a careful evaluation of the characteristics of each investment type. By considering the factors outlined above, investors can make informed choices that align with their financial aspirations and contribute to the long-term growth of their portfolios. Continuous monitoring of market trends and seeking professional advice remain crucial elements of successful real estate investment.

Published on: 2025-04-21T16:27:56.000Z
